
March / April 2005

MEDDIC-MS
Blood lead toxicity screening
Targeted performance improvement measure

Children in Medicaid are considered to be at risk for exposure to sources of lead poisioning in their living environment. For this reason, provision of blood lead toxicity testing is required for children at age one and two years and up to age six if elevated levels or risk factors have been identified.
In the Wisconsin Medicaid & BadgerCare HMO program, blood lead toxicity screening at age one and two years is required under the contract and is a Targeted Performance Improvement Measure in the MEDDIC-MS performance measure system.
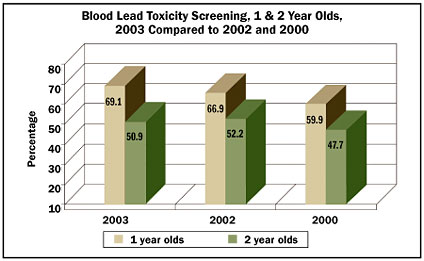
Blood lead toxicity screening rates improved between 2000 and 2003 for both one- and two-year-old children. The screening rate for one-year-old children increased from 59.9 percent in 2000 to 69.1 percent in 2003. The screening rate for two-year-old children increased from 47.7 percent to 50.9 percent in the same period, although there was a slight decrease in the rate from 2002, which was 52.2 percent.
In 2001, the Department instituted the Care Analysis Project (CAP) on blood lead toxicity screening. Recipient-specific lead testing data is shared with the individual's HMO in an effort to assist HMOs with identification of children in need of lead screening. This facilitates outreach and follow-up for children who have not received screening. This effort may be a factor in the recent improvement in the lead screening rate trends.
In addition, 5 of 13 Medicaid/BadgerCare HMOs have conducted performance improvement projects on lead screening since 2000.
Return to main story:

|

